Biomedical Applications
Vision-Based Fallen Person Detection for the Elderly
Falls are serious and costly for elderly people. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention of the US reports that millions of older people, 65 and older, fall each year at least once. With this project we are working on a new, non-invasive system for fallen people detection. Our goal is to use only stereo camera data for passively sensing the environment.
The key novelty is a human fall detector which uses a CNN based human pose estimator in combination with stereo data to reconstruct the human pose in 3D and estimate the ground plane in 3D. Furthermore, a reasoning module is proposed which formulates a number of measures to reason whether a person is fallen. Based on our extensive evaluations, our system shows high accuracy and almost no miss-classification.

Publications
Solbach, Markus D., and John K. Tsotsos. “Vision-based fallen person detection for the elderly.” Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2017.
PlayBot – Hardware Design
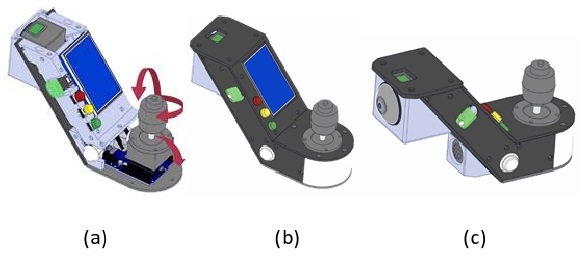
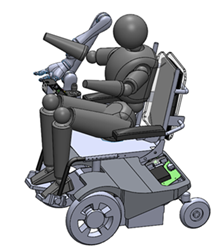
Designing and constructing a Wheelchair platform for research in application of AI in rehabilitation. PlayBot provides researcher with a platform to test and verify their Autonomous system design. Various different types of system can be tested on playbot, such as Person Following [1], head pose recognition[2], visually guiding the wheelchair [3] etc. The wheelchair is designed with various safety measures building, such as remote shutdown, power drainage checks etc. These measures are included to operate safely inside the lab. The design incorporates low level designs as well, such as designing the smart joystick, a RTOS microcontroller for control, RC remote etc.
References
[1] Chen, Bao Xin, Raghavender Sahdev, and John K. Tsotsos. “Person following robot using selected online ada-boosting with stereo camera.” 2017 14th Conference on Computer and Robot Vision (CRV). IEEE, 2017.
[2] Bauckhage, Christian, et al. “Fast learning for customizable head pose recognition in robotic wheelchair control.” 7th International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FGR06). IEEE, 2006.
[3] Rotenstein, A., et al. “Towards the dream of intelligent, visually-guided wheelchairs.” Proc. 2nd Int’l Conf. on Technology and Aging. 2007.
PlayBot – Interface Design
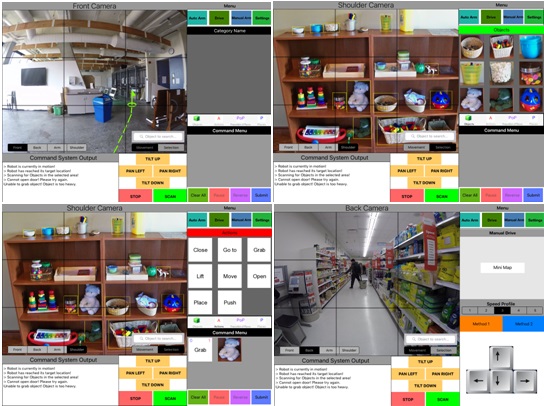
Goal 1: Design a touch screen user interface for the iPad that allows users with limited upper body mobility (e.g. elderly, user’s with a physical disability) to control an intelligent power wheelchair that has a wheelchair mounted robotic arm (WMRA) attached to it with the desire/intent to assist users in their activities of daily living (ADL). Some of the features that are part of the interface include: Central control (i.e. enable/disable of other interfaces, settings configuration); Capability to select a 2D pixel, which translates to a 3D world coordinate, from the live camera field of view to be passed on to the autonomous navigation system (Figure 1); Global area specification (e.g. kitchen, living room, bedroom) whose world coordinates are passed on to the autonomous navigation system; Scraping objects (Figure 2), via detection and recognition algorithms, in the scene (camera’s field of view) which are then fed to a local database and displayed to the user allowing them to select from the list of objects (i.e. cropped images) and form high level commands (Figure 3) that are passed to the wheelchair mounted robotic arm system for it to execute the given command. Example tasks would be to: pickup cup from table, open the door, put bottle on top of the desk but next to the plate, etc.
Publications
Tsotsos, J.K., Verghese, G., Dickinson, S., Jenkin, M., Jepson, A., Milios, E., Nuflo, F., Stevenson, S., Black, M., Metaxas, D., Culhane, S., Ye, Y., Mann, R., PLAYBOT: A visually-guided robot to assist physically disabled children in play, Image & Vision Computing Journal, 16, p275-292, April 1998.
Fine, G., Tsotsos, J.K, Examining The Feasibility Of Face Gesture Detection For Monitoring Of Users Of Autonomous Wheelchairs, Ubiquitous Computing And Communication Journal, Special Issue of Media Solutions that Improve Accessibility to Disabled Users, 2010.
Andreopoulos, A., Tsotsos, J.K., Active Vision for Door Localization and Door Opening using Playbot: A Computer Controlled Wheelchair for People with Mobility Impairments, Fifth Canadian Conference on Computer and Robot Vision, Windsor, Ont., May 28-30, 2008.
Andreopoulos, A., Tsotsos, J.K., A Framework for Door Localization and Door Opening Using a Robotic Wheelchair for People Living with Mobility Impairments, RSS 2007 Manipulation Workshop: Sensing and Adapting to the Real World, Atlanta, Jun. 30, 2007.
Rotenstein, A., Andreopoulos, A., Fazl, E., Jacob, D., Robinson, M., Shubina, K., Zhu, Y., Tsotsos, J.K., Towards the dream of intelligent, visually-guided wheelchairs, Proc. 2nd International Conference on Technology and Aging, Toronto, Can. June, 2007.
Tsotsos, J. K. and Dickinson, S. and Jenkin, M. and Milios, E. and Jepson, A. and Down, B. and Amdur, E. and Stevenson, S. and Black, M. and Metaxas, D. and Cooperstock, J. and Culhane, S. and Nuflo, F. and Verghese, G. and Wai, W. and Wilkes, D. and Ye, Y., ‘The PLAYBOT Project’, In J. Aronis Ed., Proc. IJCAI Workshop on AI Applications for Disabled People, Montreal, 1995.