Pedestrian intention estimation
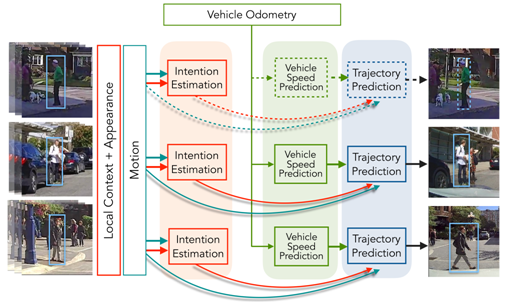
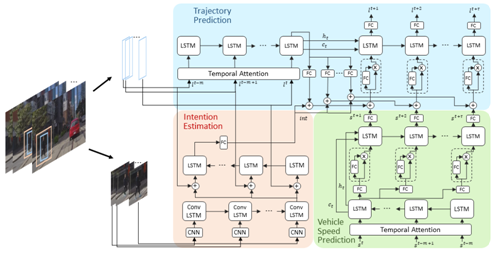
The objective of this project is to develop methods to predict underlying intention of pedestrians on the road. Understanding the intention helps distinguish between pedestrians that will potentially cross the street and the ones that will not do so, e.g. those waiting for a bus. To achieve this objective we want to establish a baseline by asking human participants to observe pedestrians under various conditions and tell us what the the intention of the pedestrians were. We want to use this information to train an intention estimation model and examine how it can improve the prediction of pedestrians’ trajectories and actions.
Key Results
Humans are very good at estimating the intention of pedestrians. Overall, there is a high degree of agreement among human observers regarding the intentions of people on the road. From a practical perspective, we found that including a mechanism to estimate pedestrian intention in a trajectory prediction framework can improve the results.
Publications
A. Rasouli, I. Kotseruba, T. Kunic, and J. Tsotsos, “PIE: A Large-Scale Dataset and Models for Pedestrian Intention Estimation and Trajectory Prediction”, ICCV 2019
A. Rasouli, I. Kotseruba, and J. K. Tsotsos, “Pedestrian Action Anticipation using Contextual Feature Fusion in Stacked RNNs”, BMVC 2019.