Eye Movements
STAR-FC
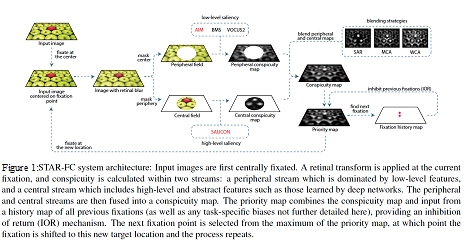
The Selective Tuning Attentive Reference Fixation Control (STAR-FC) model provides a dynamic representation of attentional priority as it predicts an explicit saccadic sequence over visual input, moving beyond a static saliency representation for fixation prediction. STAR-FC provides a link between saliency and higher level models of visual cognition, and serves as a useful module for a broader active vision architecture.
equence over visual input, moving beyond a static saliency representation for fixation prediction. STAR-FC provides a link between saliency and higher level models of visual cognition, and serves as a useful module for a broader active vision architecture.
Key results
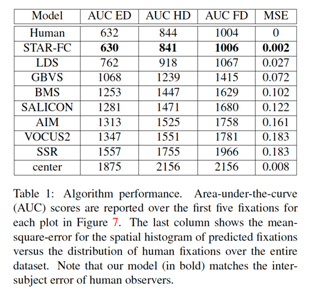
– High fidelity reproduction of the first five fixations over an image
– Qualitatively more natural sequence structure for long duration saccade sequences
Publications
Calden Wloka, Iuliia Kotseruba, and John K. Tsotsos (2018) Active Fixation Control to Predict Saccade Sequences. Proc. of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)
John K. Tsotsos, Iuliia Kotseruba, and Calden Wloka (2016) A Focus on Selection for Fixation. Journal of Eye Movement Research 9(5):2,1-34
Code is available from https://github.com/TsotsosLab/STAR-FC
For more information visit:
http://www.cse.yorku.ca/~calden/projects/fixation_control.html
STAR-FCT
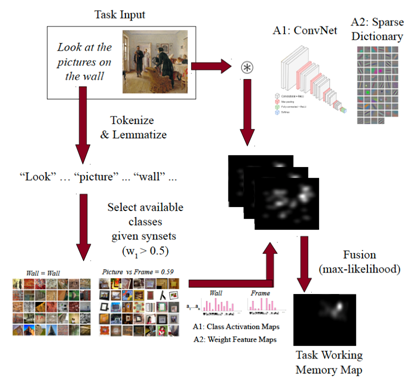
In this work we propose an architecture to enable tuning of attentional processing mechanisms to adapt vision given specific task instructions. We will extend to the Selective Tuning Attentive Reference Fixation Controller (STAR-FC) by incorporating:
– Long-Term Memory (LTM) for Symbolic and Visual Representations
– Task Working Memory (tWM) for Location bias with respect task specification
– Visual Task Executive (vTE) to Fetch methods from LTM to Hierarchy & tWM
We hope to provide low- and high-level feature basis for the visual memory representations, to define a hierarchical lexico-semantic memory explaining the task specification, determine influences of task over fixations (including memory, covert and overt attention).
This work is led by our collaborator, Dr. David Berga, Computer Vision Center, Autonomous University of Barcelona, Spain.
Publications
Berga D, Wloka C, Tsotsos JK and Lassonde School of Engineering – York University. Modeling task influences for saccade sequence and visual relevance prediction. F1000Research 2019, 8:820 (poster) (https://doi.org/10.7490/f1000research.1116873.1)